From the 1970s until 2000, the Sadova-Corabia irrigation system watered over 70,000 hectares of land in Romania’s Dolj and Olt counties. A set of pipelines that brought water from the Danube, the system turned the area from a sandy region predominantly used for vineyards into a fruit and vegetable paradise. Little by little, however, the system was abandoned; now only segments of it are still working.
Agriculture in the area has changed, as has the environment. Today the Sadova-Corabia region is known not just as the homeland of Romania’s famous Dăbuleni watermelons, but also as the ‘Romanian Sahara’. Together with the south of Moldavia, Dobrogea and the Danubian Plain, it is one of the regions in Romania most affected by desertification.
Anthropologist Bogdan Iancu has been researching the irrigation system in southern Romania for several years. Scena9 sat down with him to talk about drought, Romania’s communist-era irrigation systems, and the local reconstruction of agriculture after their decline. The interview has been edited for clarity.
Oana Filip: How did your interest in drought arise?
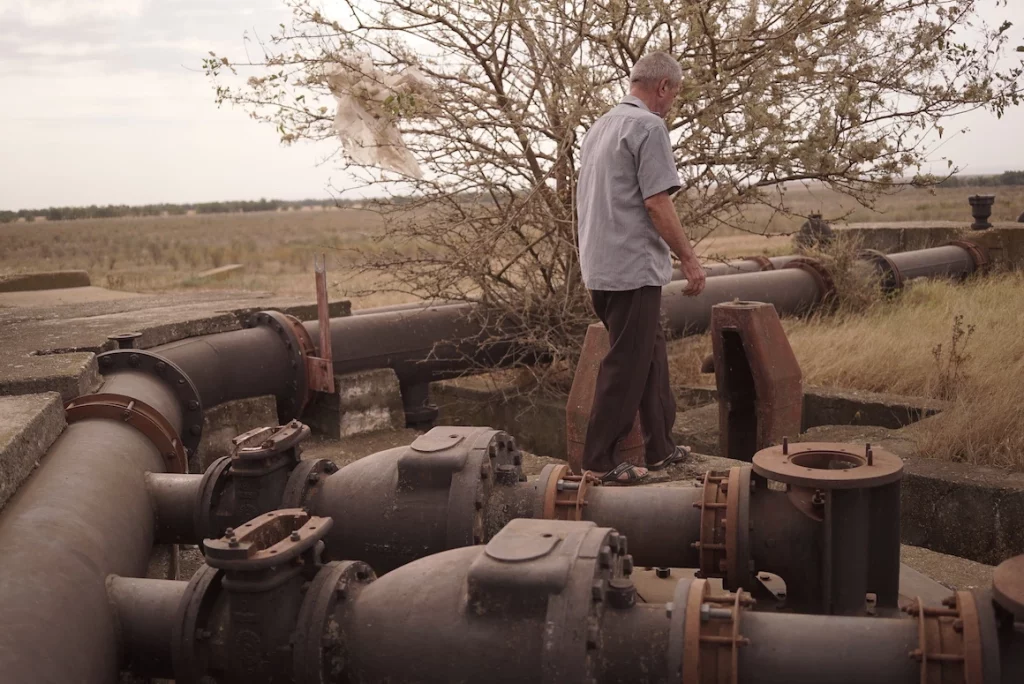

Image copyright Maria Bălănean / Scena9
Bogdan Iancu: Rather by accident. Around seven years ago I was in the Danube port of Corabia for another research project, and at one point I heard a student talking at a table with a local, who was telling him about the 2005 floods and the irrigation systems in the area. The man also wanted to talk to me and show me the systems. It was an extremely hot summer and I thought it was very interesting to talk about irrigation and drought.
I myself come from the area of Corabia-Dăbuleni. My grandparents lived in a village a bit north of the Danube floodplains, where there was an irrigation system with canals. This was where I learned to swim. The encounter somehow reactivated a personal story about the frequent droughts of that time and the summers I spent there. A lot of people in the area told us that the emergence of irrigation systems in the ’60s and ’70s led to more employment in agriculture. For them it was a kind of local miracle. As I realized that droughts were becoming more frequent and widespread, I became certain that this could be a research topic.
The following year I started my own project. In the first two or three years, I was more interested in the infrastructure and its decline, the meanings it held for the locals and the people employed in the irrigation system, and how this involved their perceptions of changes in the local microclimate. Later, I became interested in the fact that people began to migrate out of the area because of the dismantling and privatization of the former collective or state-owned farms.
I then started looking at how seasonal workers who had left for Italy, Spain, Germany or Great Britain had begun to come back to work in agriculture and start their own small vegetable farms. I was interested in how they started to develop the area, this time thanks to a few wells that have been drilled deep into the ground. So, somehow, the formerly horizontal water supply has now become vertical. This could have some rather unfortunate environmental implications in the future, because too many drilled wells that are not systematically planned can cause substances used in agriculture to spill into the ground water.
How has the locals’ relationship with water changed with the disappearance of the irrigation system and the increasing frequency of droughts?
The irrigation system had a hydro-social dimension. Water was primarily linked to agriculture and the planned socialist system. For a long time, the locals saw the system as the reason for the appearance and cultivation of fruits and vegetables they had never known before. For ten years after 1990, the irrigation network still worked and helped people farm on small plots of land, in subsistence agriculture, so that they could still sell vegetables in nearby towns. But after 2000 the state increased the price of water and cut subsidies. When the system collapsed, the ecosystem built around it collapsed along with it.
At that time, something else was going on as well. The system was being fragmented through a form of – let’s say partial – privatization of the water pumping stations. The irrigators’ associations received loans via the World Bank. These associations did not work very well, especially since the people there had just emerged from the collective farming system, and political elites deliberately caused all forms of collective action to lose credibility after the ’90s.
Because the irrigation system was no longer being used, or being used at much lower parameters than before, it no longer seemed functional. Bereft of resources, the local population saw the remaining infrastructure as a resource and sold it for scrap. It became even more difficult to use the irrigation system. This caused people to migrate abroad. The first waves of ‘strawberry pickers’ have only recently started coming back, perhaps in the past six or seven years, bringing in the money they have made in Italy or Spain.
People have to be empowered in relation to the water they need. So these seasonal workers began digging their own wells. They have lost all hope that the state can still provide this water for them. They saw that in the Romanian Danubian Plain, thousands, tens of thousands of hectares of land were sold off cheaply to foreign companies that receive water for free, because they take it from the drainage canals. This caused even greater frustration for the locals, who not only look down on the new technologies that these companies use, but also resent their privilege of receiving free water from the Romanian state.
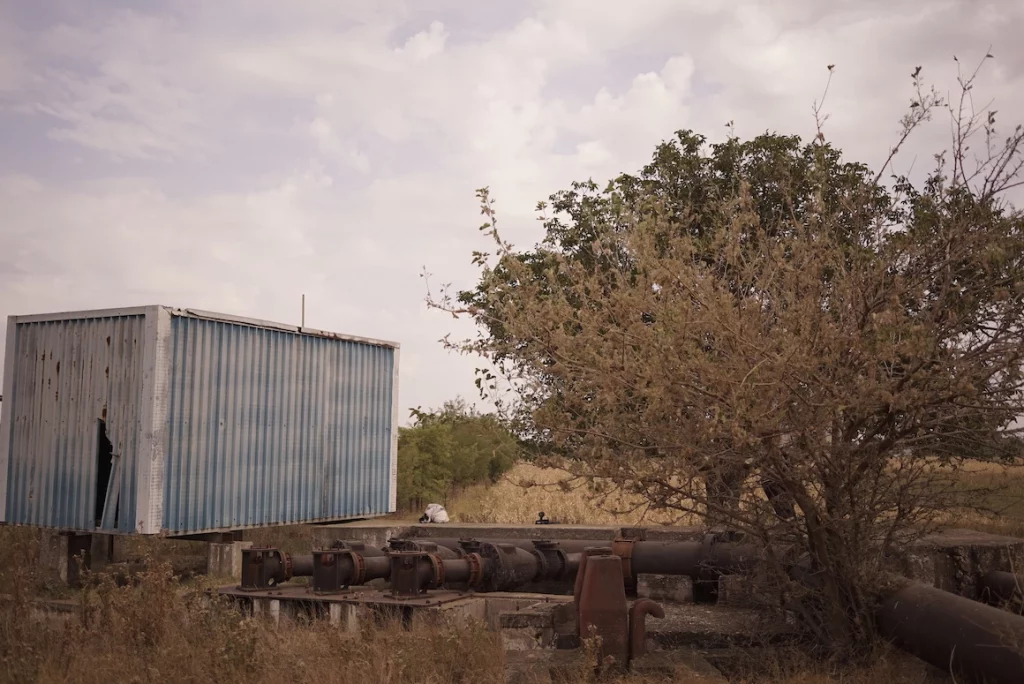
Image copyright Maria Bălănean / Scena9
How do you see the future of the area?
It’s difficult to say. In the short term, I think the area will partially develop. But, at the same time, I think problems could arise from too many exploitations.
The number of private wells will probably increase. Some very large companies in Romania are lobbying Brussels to accept the inclusion of wells drilled into underground aquifers (geological formations that store groundwater) into the irrigation strategy being developed by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development. This would mean ten years of semi-subsistence, or slightly above semi-subsistence agriculture, where the former ‘strawberry pickers’ turn into successful small farmers. We’ve already seen this in the villages on the Sadova-Corabia system. But we have no way of knowing how long this will last, and how much pressure these aquifers would be subjected to. There is a risk that they might get contaminated, because they function like pores, and the water resulting from agricultural activities, which contains nitrites and nitrates, could get in there and cause problems.
In Spain, for instance, they are very cautious about drilling wells. Arrests have been made. It’s a political issue that contributed to the defeat of Pedro Sanchez’s Socialist party in the last elections. Many farmers in Spain privileged to have access to water could dig a well wherever they wanted, but now found themselves faced with this rather drastic law. And the People’s Party promised them that they would be able to continue digging wells.
At the Dăbuleni Agricultural Research Station, for example, they are experimenting with exotic crops better adapted to desertification, such as dates, kiwis and a certain type of banana. Do you think people could adopt new cultures in Sadova-Corabia too?
This already happened decades ago. With the advent of the irrigation system, people were forced to be open to cultivating vegetables and fruits they had never seen before. Someone told me how, when they ate the first eggplants, they didn’t know what to do with them, they seemed bitter. Even tomatoes, which to us seem always to have been eaten there, were only introduced in the ’60s. One person told me that when he first tried a tomato he thought it tasted like soap. But if their grandparents or parents could adapt, so will people today. Besides, most have worked in agriculture abroad with this kind of fruit.
Have you seen any irrigation best practices that you think would be suitable for the situation in the Sadova-Corabia area?
I think one such example is micro-agriculture, which is employed on smaller plots in Italy, for instance. There are also micro farms in Sadova-Corabia that produce organic, ecological, sustainable products and so on. And there are a few cooperatives that work quite well, some of them supply tomatoes for the Belgian-owned supermarket chain Mega Image, for example.
Spain, on the other hand, is not a best practice model. Spain is a devourer of water resources in an absolutely unsustainable way. We’re already seeing that the Tagus (the longest river in the Iberian peninsula and an important source for irrigation) is endangered by large-scale agriculture. In the 1990s, there was small and medium-sized farming there, and I think there should be a return to that. Obviously, the economists say it’s not profitable, but it’s time to think about a decrease and not an increase, which is always cannibalistic. This kind of farming, on a medium or small scale, should also bring this irrigation system back into focus.
Unfortunately, it’s unclear for how much longer the Sadova-Corabia system will be able to function. It has an outlet in the Danube, which dries up in the summer and is not permanently supplied with water, as it was during the socialist period. Last year, for example, irrigation electricians and mechanics working on the Danube encountered problems, because the main canal poured water into the Danube, instead of collecting from it. If the Danube is no longer a sustainable source for irrigation canals (and not just in Romania), the alternative lies in the different management of water resources.
In the multimedia exhibition based on the project that you organized last year, there was a notion of how grand socialist projects obfuscated life narratives, and how human stories were lost to anonymity. What life narratives are being lost or hidden now, in this larger discussion of drought and desertification in the area?
I met a woman who during communism had managed a farm where they grew peaches that were then exported to Germany and Czechoslovakia. She told me that local vegetables were exported to Great Britain; and that this export was even stipulated by the two countries. Over 200 British technicians and experts lived in Sadova-Corabia for about four years. The story of these people, these British experts, not just the Romanian ones, and how they collaborated is completely lost to history.
In the ’70s, these people were a sort of agricultural vanguard. They were trying to propose a productive model of agriculture, a break from the post-feudal, post-war past. There were people who worked at the pipe factory and built those gigantic pipes through which water was collected from the Danube. Today, there are still people who continue to make enormous efforts to do what needs to be done. The mayor of Urzica, for example, encourages locals to sell or give away plots of land for afforestation, and the town hall is even trying to deploy its own afforestation projects.
I have seen journalists travel to the area for two days, come back and report that socialism destroyed everything. Obviously, lakes were drained and the environmental toll was very high. At the same time, that era brought unlimited water to many areas where it was previously lacking. Acacia forests were planted. Biologists say they’re no good, as they actually consume water from the soil; but foresters everywhere defend them and say they provide moisture.
One way or another, all these stories should be told. As should the stories of the people who went abroad for work and are coming back. These so-called ‘strawberry pickers’ or ‘seasonals’, whose lives we know nothing about, because the Romanian state doesn’t believe that five million Romanians who went to work abroad deserve the attention.
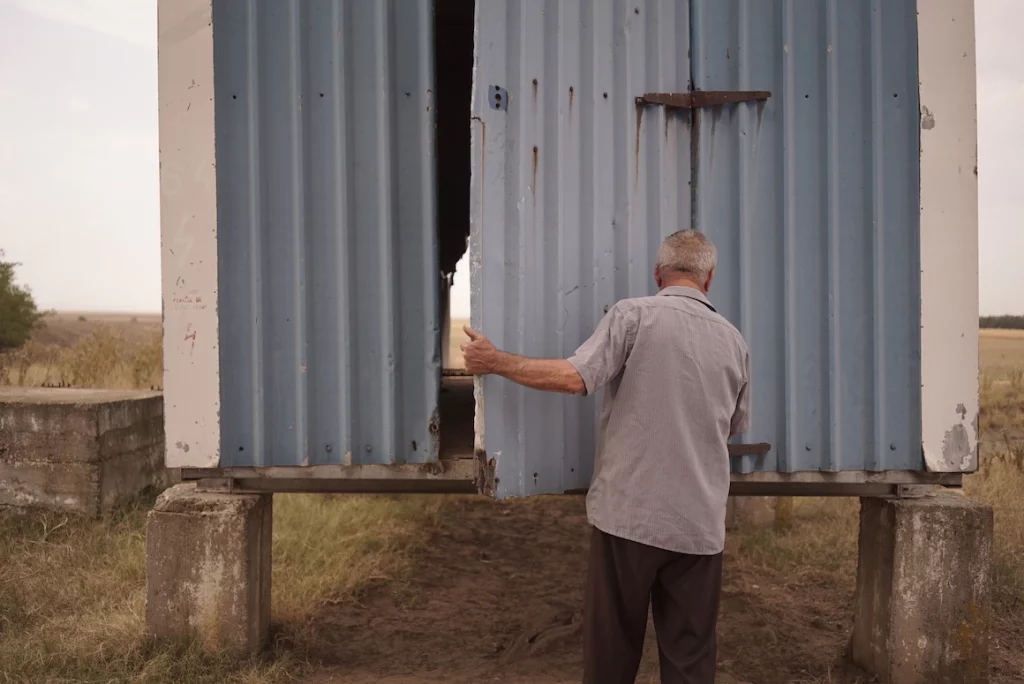

Image copyright Maria Bălănean / Scena9
When I went to the Dăbuleni research station, many of the researchers had grown up there and had a personal connection to the area and a notion that they were working for the place where they grew up. How does the connection between the locals and the environment change, when so many choose to work abroad?
This is where things intersect. These people have parents who tell us that for them the emergence of the irrigation system was similar to what happened in Israel, a country that has problems with its soil and that managed to make it better with the aid of water improvement systems. They saw that desert repopulated, greened, diversified, and they saw a greater complexity in the kinds of crops they can grow. They got predictability, i.e. permanent jobs at state agricultural enterprises, or jobs that allowed them to work at home, at the agricultural production cooperative (CAP).
One thing I didn’t know before this research was that peasants who met their agricultural production quota were given 22 acres of land that they could work within the CAPs, with fertilizer from the CAPs, and irrigated with water from CAPs. One person I talked to even drove a truck contracted by the state and sold watermelons in Cluj, Sibiu, Râmnicu Vâlcea, and Bucharest in the 1980s and 1990s. And he wasn’t the only one.
For them, the irrigation system was not only associated with farms, but also the related industries – pipeline factories, factories making tiles that lined the irrigation channels. It was a flourishing new ecosystem. But once this system collapsed, they also came to associate it with the degradation of the environment. I spoke to a local who said that when the system worked, he didn’t feel the summer heat, even though the temperatures were just as high, because of the water in the canal network.
The absence of water is like the absence of blood – without it, an organism can no longer metabolize. And then, naturally, the young people decided to leave. But this was not a permanent departure. They went to Spain, for example, they saw vertical water there, and they said, ‘Look, we can make our own wells, we don’t need to wait around for horizontal water.’
Why, as a state, have we failed to come up with an irrigation project today as ambitious as Sadova-Corabia in its time?
There’s more to it than just this one system. There are about a hundred or so chain irrigation systems that start in this area, from south of Resita all the way to Dobrogea. The problem is that these irrigation systems were in full boom before the 1990s. Now, don’t think I believe that only irrigation systems can ensure good crops. I think they should be seen as part of a mixed bag of solutions. The problem is not that no more irrigation systems have been built, but that the old ones have not been preserved, optimized or modernized. Private interests were prioritized, especially those of a very large class of landowners, and land-grabbing was prioritized to the detriment of working on smaller plots of land. And so, such infrastructures were abandoned, because the big players can afford super-performant extractive technologies.
How do you see urban dwellers relate to droughts and irrigation?
I have seen many of them ridiculing people in the countryside and finding it unacceptable that they use municipal water handed to them for irrigation; but, at the same time, none of them disclose the amount of water they use on their lawns, which are worthless grass. Obviously, it’s easier to laugh from inside an office and to think that people are being irrational than to understand that they’re selling tomatoes that they would have otherwise been unable to grow.
As climate change intensifies, droughts will become more frequent. Will we see better cooperation in the face of this new reality, or more division?
In the next five to six years I think we will see more competition for water and the criminalization of our fellow water-users. But I think that this is where the role of the media comes in. It should abandon the logic of only showing us the big, scary monster called climate change. Rather, it should detail how these climate changes are occurring at the grassroots level. I think both the press and the state should work on research and popularization, on disseminating information that talks about these effects.
I don’t think that anything can be done without pedagogies. Yes, during the socialist period these pedagogies were abused, sometimes enforced with actual machine guns, and that was tragic. But today we don’t see any kind of pedagogy, any kind of relating. None of the measures that need to be implemented are socialized. People are not being called to their village cultural center to be told: ‘Here’s what we want to do.’ The cultural center is now only used for weddings. Some radical forms of pedagogy should be devised and disseminated locally, so that people understand the invisible price of water.